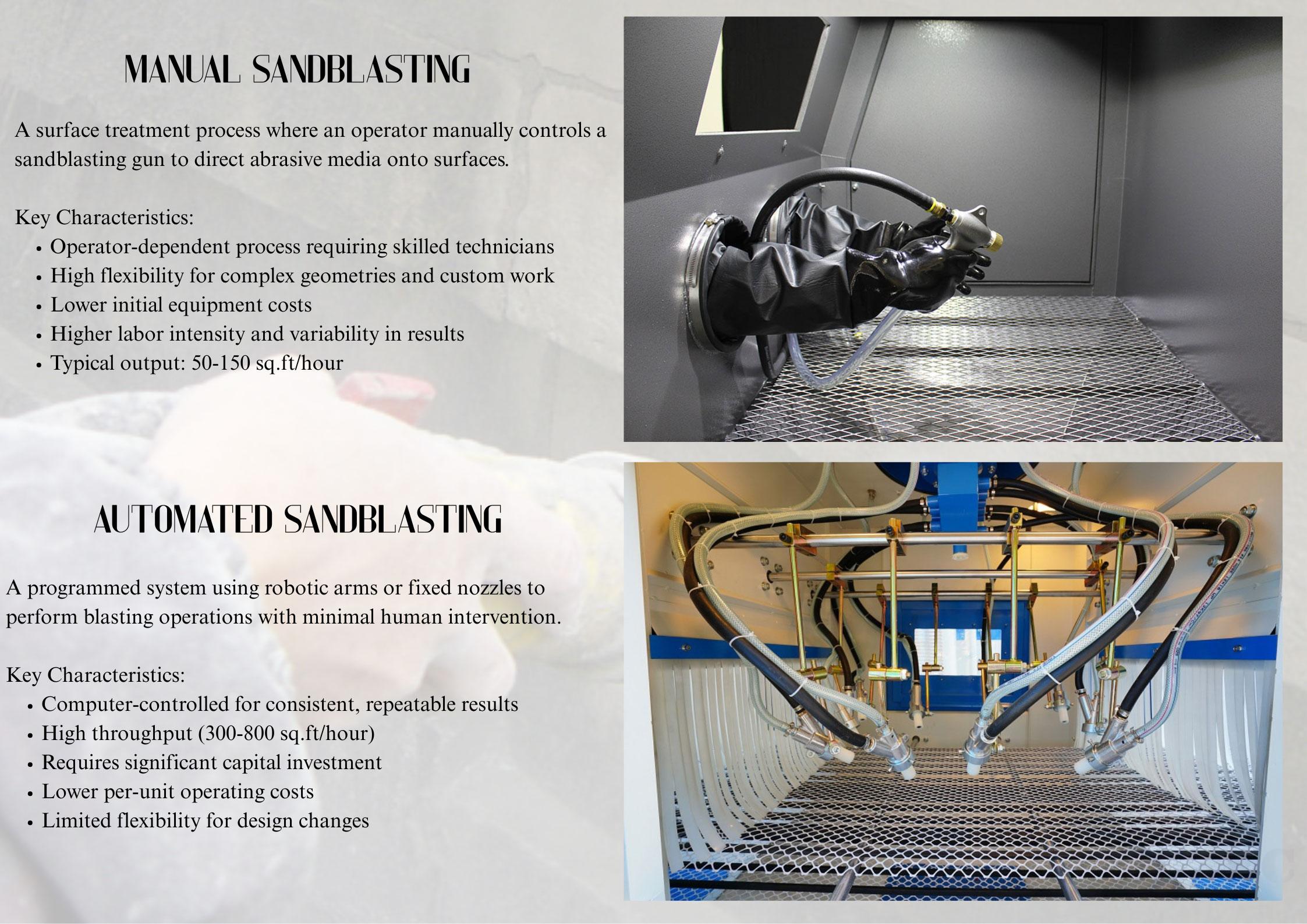
Automated vs. Manual Sandblasting: Which Nozzle Type Fits Your Operation
Automated vs. Manual Sandblasting: Which Nozzle Type Fits Your Operation

Introduction: The Great Automation Decision
In modern surface preparation, the choice between automated and manual sandblasting systems represents a critical crossroads for operational efficiency. This comprehensive analysis examines the five fundamental factors that determine which nozzle type - and by extension, which blasting method - delivers optimal performance for your specific application. With 20% of industrial operations now transitioning to automated solutions annually, understanding these key differences becomes essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
1. Nozzle Durability: The Wear Resistance Imperative
Material Science Behind Operational Longevity
Automated systems demand superior nozzle materials due to their continuous operation:
✅Tungsten carbide (WC): 500-1,000 hour lifespan under constant use
✅Boron carbide (B₄C): 800-1,500 hours for ultra-high-end systems
✅Ceramic: Only suitable for manual intermittent use (100-200 hours)
Technical Insight:
The cobalt matrix in tungsten carbide nozzles absorbs vibrational energy in robotic systems, while ceramic's crystalline structure fractures under sustained mechanical stress. Automated operations experience 10× higher nozzle wear rates than manual applications.
Case Example:
German automotive supplier Continental reduced nozzle replacement costs by 68% after switching to tungsten carbide in their robotic blasting cells.

2. Precision Engineering Requirements
Tolerance Standards Across Applications
Specification | Automated Nozzles | Manual Nozzles |
Bore Diameter Tolerance | ±0.01mm | ±0.05mm |
Surface Profile Consistency | Ra ±1.2μm | Ra ±3.5μm |
Angular Deviation | <0.5° | <2° |
Critical Consideration:
Venturi nozzles in automated systems maintain ±2% media velocity variance versus ±15% in manual operations, directly impacting coating adhesion standards.
3. Productivity Benchmarks
Throughput Comparison in Industrial Settings
Automated System Capabilities:
✅500-800 sq ft/hour coverage
✅30-40% faster than manual
✅10-15% media savings
Manual Operation Realities:
✅200-350 sq ft/hour
✅Better for complex geometries
✅Higher operator skill dependency
Productivity Tradeoff:
While automated systems process 2.5× more surface area, manual methods maintain superiority for intricate components like turbine blades or sculpture restoration.
4. Financial Analysis: Total Cost of Ownership
5-Year Operational Cost Breakdown
Cost Factor | Automated | Manual |
Equipment | $250,000 | $5,000 |
Nozzles (5yr) | $3,200 | $8,750 |
Labor | $75,000 | $375,000 |
Media Waste | $18,000 | $27,000 |
Total | $346,200 | $415,750 |
ROI Insight:
Automation breaks even at 14-18 months for operations blasting >400 sq ft daily. Small shops processing<100 sq ft/day find manual more economical.
5. Application-Specific Selection Guide
Decision Matrix for Common Industries
Automation Preferred:
1. Automotive (frame coating)
2. Wind turbine (tower sections)
3 . Pipeline (exterior preparation)
Manual Recommended:
1. Aerospace (engine components)
2 .Art conservation (delicate surfaces)
3 . Prototype development
Emerging Solution:
Hybrid systems now combine robotic consistency with manual flexibility - particularly effective in shipbuilding for hull vs. compartment work.
Implementation Roadmap
Transitioning Between Systems
Step 1: Conduct 30-day throughput analysis
Step 2: Validate nozzle compatibility
Step 3: Pilot test with 1 automated cell
Step 4: Train technicians on dual systems
Step 5: Full-scale implementation
This technical and financial analysis provides operations managers with a data-driven framework for evaluating sandblasting automation. By combining measurable performance metrics with real-world implementation case studies, this guide serves as both a strategic planning tool and a practical transition manual.













